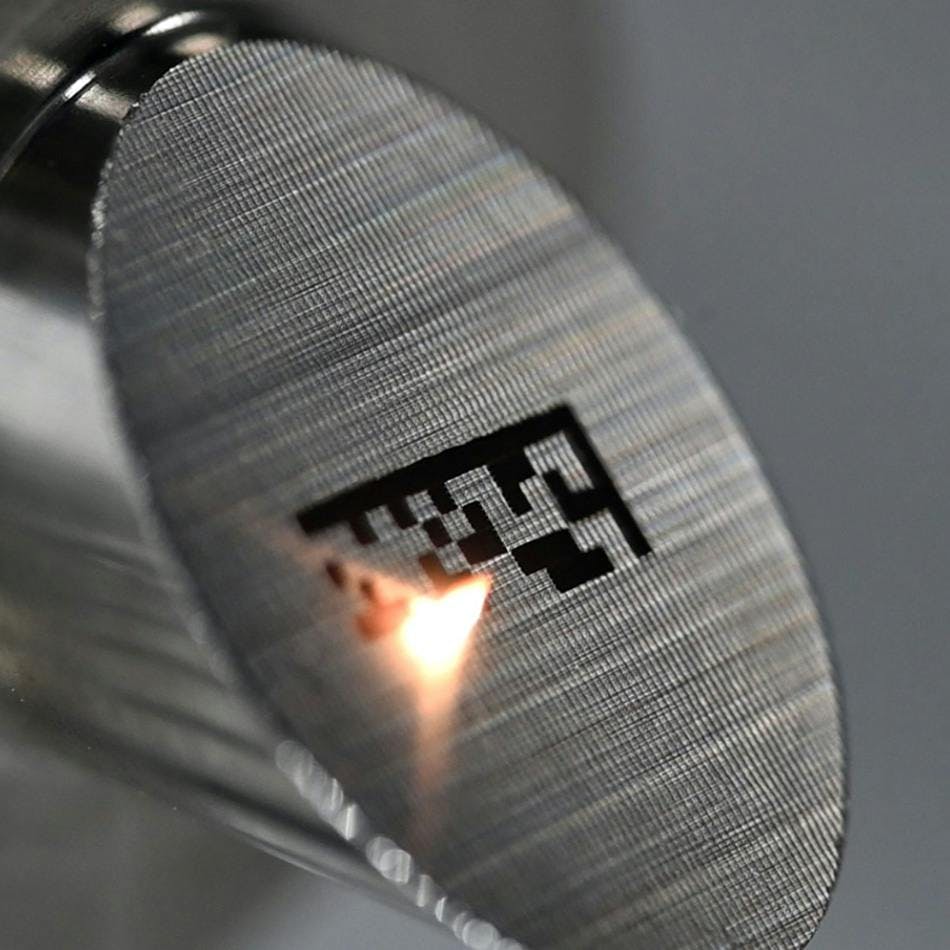
Where is laser engraving used?
The laser engraving method is most often used in Direct Part Marking (DPM); a process used to track the lifecycle of parts and components as they progress throughout the manufacturing process and supply chain journey. As governmental regulations become increasingly stringent, manufacturing and production houses find that the engraving process offers a permanent, robust and speedy solution for marking the relevant information needed for traceability. In particular, to help resolve liability issues in the event of warranty disputes or product recalls.
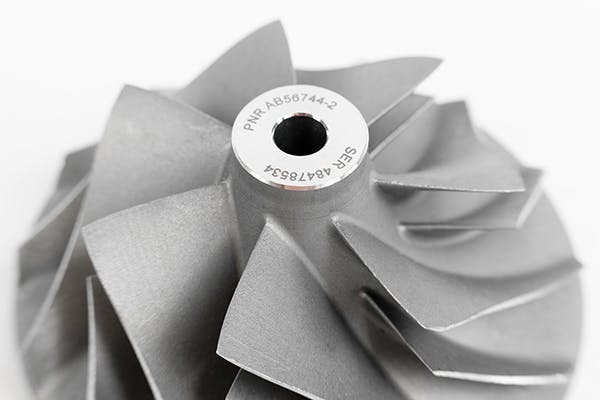
Direct part marking has become commonplace in many industries, including the automotive, medical and aerospace sectors.
For example, a car manufacturer would need to engrave individual components, subassembly, system and the final car assembly codes, in order to track the manufacturing process of each car. The laser engraving method is ideal for this type of marking, as it is a quick and permanent solution that is not affected over time by the heat of the engine.
Similarly, tools and devices within the medical industry need to comply with the Unique Device Identifier (UDI) guidelines. Parts and products such as hip stems, bone plats, catheters and surgical tools, must have a permanent code for traceability and quality assurance. The non-contact laser engraving technique is perfect for such an application. It creates a permanent mark that would last for years and is corrosion-resistant.